| Java Stream对List分组、排序、组内排序 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › groupby 排序并只取前10条 › Java Stream对List分组、排序、组内排序 |
Java Stream对List分组、排序、组内排序
|
项目场景:
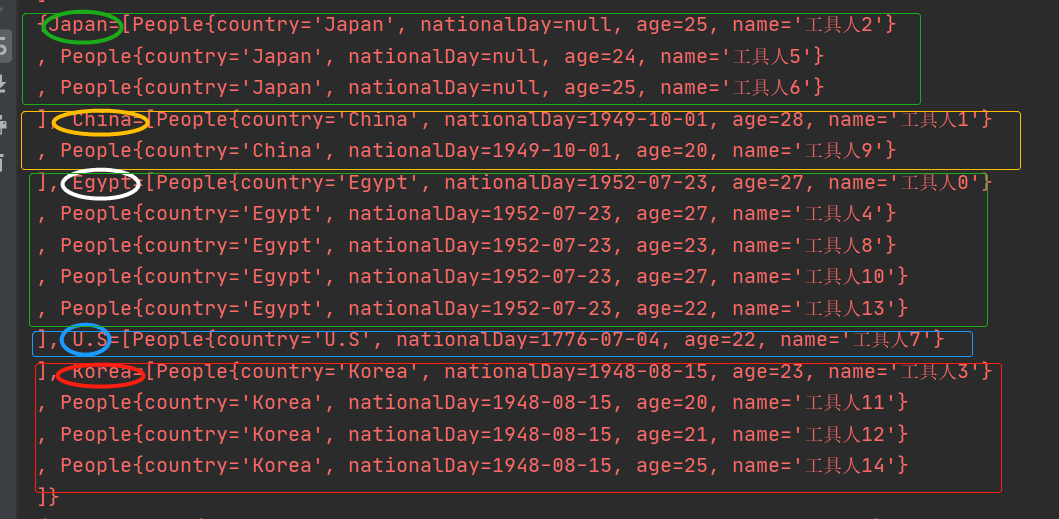
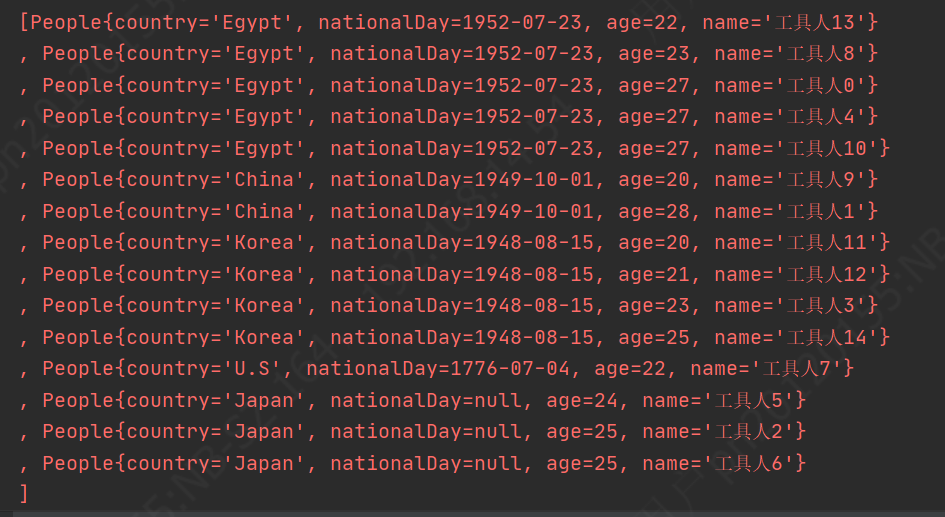
前段时间遇到了一个业务场景,要对List对象列表进行较复杂的排序操作:首先要对列表根据对象属性A进行分组,然后要对分组后的每组内的对象属性B(每组的属性B值相同,可能为空)对组进行排序,然后每组组内要对属性C进行排序 这里的对象为People类属性为: @Data public class People { /**国家*/ private String country; /**国庆*/ private Date nationalDay; /**年龄*/ private Integer age; /**姓名*/ private String name; }即原始数据如下: [People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=27, name='工具人0'} , People{country='China', nationalDay=1949-10-01, age=28, name='工具人1'} , People{country='Japan', nationalDay=null, age=25, name='工具人2'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=23, name='工具人3'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=27, name='工具人4'} , People{country='Japan', nationalDay=null, age=24, name='工具人5'} , People{country='Japan', nationalDay=null, age=25, name='工具人6'} , People{country='U.S', nationalDay=1776-07-04, age=22, name='工具人7'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=23, name='工具人8'} , People{country='China', nationalDay=1949-10-01, age=20, name='工具人9'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=27, name='工具人10'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=20, name='工具人11'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=21, name='工具人12'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=22, name='工具人13'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=25, name='工具人14'} ]目标数据为:即先对对象的country进行分组,然后用nationalDay对每组进行倒序(nationalDay属性为空放最后),每组组内对age进行升序 [People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=22, name='工具人13'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=23, name='工具人8'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=27, name='工具人0'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=27, name='工具人4'} , People{country='Egypt', nationalDay=1952-07-23, age=27, name='工具人10'} , People{country='China', nationalDay=1949-10-01, age=20, name='工具人9'} , People{country='China', nationalDay=1949-10-01, age=28, name='工具人1'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=20, name='工具人11'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=21, name='工具人12'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=23, name='工具人3'} , People{country='Korea', nationalDay=1948-08-15, age=25, name='工具人14'} , People{country='U.S', nationalDay=1776-07-04, age=22, name='工具人7'} , People{country='Japan', nationalDay=null, age=24, name='工具人5'} , People{country='Japan', nationalDay=null, age=25, name='工具人2'} , People{country='Japan', nationalDay=null, age=25, name='工具人6'} ]
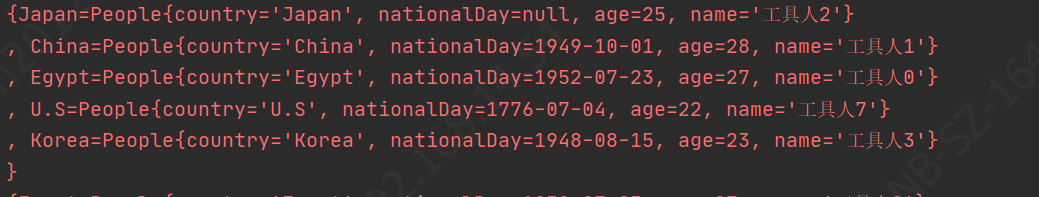
我的方案是通过Stream对列表进行分组排序等操作达到预期结果: 1、 country分组分组为Map集合key-value值为country属性-同country属性的列表List // 1、country分组 Map countryGroupMap = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getCountry)); System.err.println(countryGroupMap);
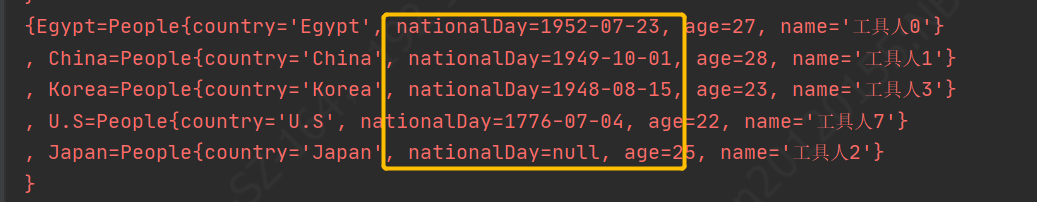
注意:用LinkedHashMap保存,因为HashMap是根据key计算hash值设置元素存储位置的是无序的,故应用有序map保存排序后数据 // 对分组后的map根据nationalDay倒序(birthday可能为空null放最后) Map linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap(); countryGroupGetOneMap.entrySet().stream().sorted( Map.Entry.comparingByValue( Comparator.comparing( People::getNationalDay, Comparator.nullsFirst(Date::compareTo) ) ).reversed() ).forEachOrdered(e -> linkedHashMap.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue())); System.err.println(linkedHashMap);
附上完整代码: /** * @author zg * @create 2021/8/24 19:19 */ public class GroupTanSortExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // 生成乱序的People对象列表 List peopleList = GroupTanSortExample.randomPeopleList(15); System.err.println(peopleList); // 1、country分组 Map countryGroupMap = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getCountry)); System.err.println(countryGroupMap); // 2、country分组每组取一条 Map countryGroupGetOneMap = peopleList.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy( People::getCountry,Collectors.collectingAndThen( Collectors.reducing((c1, c2) -> c1), Optional::get) ) ); System.err.println(countryGroupGetOneMap); // 3、对分组后的map根据nationalDay倒序(nationalDay可能为空null放最后) Map linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap(); countryGroupGetOneMap.entrySet().stream().sorted( Map.Entry.comparingByValue( Comparator.comparing( People::getNationalDay, Comparator.nullsFirst(Date::compareTo) ) ).reversed() ).forEachOrdered(e -> linkedHashMap.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue())); System.err.println(linkedHashMap); // 4、获取根据 nationalDay 排序后的 country列表 List nationalDaySortCountryGroupCountryList = new ArrayList(linkedHashMap.keySet()); // 5、根据country列表 获取完整分组、排序、排序类表(每组再根据年龄升序) List finalPeopleGroupSortList = new ArrayList(); for (String country : nationalDaySortCountryGroupCountryList) { // 每组再根据年龄升序 List ageSortGroup = countryGroupMap.get(country).stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList()); finalPeopleGroupSortList.addAll(ageSortGroup); } System.err.println(finalPeopleGroupSortList); } // 生成乱序的People对象 public static List randomPeopleList(int size) { List list = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { People people = new People(); people.setName("工具人" + i); int num = (int) (Math.random() * 10 % 5); people.setAge(20 + (int) (Math.random() * 10 % 9)); switch (num) { case 0:people.setCountry("China");people.setNationalDay(parserDate("1949-10-01 00:00:00"));break; case 1:people.setCountry("Japan");people.setNationalDay(null);break; case 2:people.setCountry("U.S");people.setNationalDay(parserDate("1776-07-04 00:00:00"));break; case 3:people.setCountry("Korea");people.setNationalDay(parserDate("1948-08-15 00:00:00"));break; case 4:people.setCountry("Egypt");people.setNationalDay(parserDate("1952-07-23 00:00:00"));break; default:; } list.add(people); } return list; } // 字符串解析为日期 public static Date parserDate(String dateStr) { Date date = null; try { date = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy-MM-dd HH:mm:mm").parse(dateStr); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return date; } }感觉目标是达到了,但是代码还是太冗长,Stream肯定还有更方便的方法,期待更简洁 更优雅的实现方式 |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们